Land Use Science in Action

Wildfire risk varies with shifting landcover and land use practices in southern Greece
Diverse landcover in the Mediterranean region necessitates localized approaches to reduce fire risk
- Urgent need for fire risk analyses given projected increase in Mediterranean wildfire activity
- Landcover and land use changes can both increase and decrease fire risk
- Remote sensing, combined with fire simulation modeling, can identify areas with high wildfire exposure and detrimental impacts
- NASA’s Earth observation record provides critical data for assessing risk change over time
- Modeled fire risk is essential for guiding landowner and resource manager decision making

ENABLING HARM REDUCTION FROM EXTREME HEAT IN A WARMING CLIMATE
- The Arabian Peninsula already suffers from the most extreme heat on the planet.
- Climate Chance and Land-Cover and Land-Use Change are amplifying extreme heat across the Arabian Peninsula, impacting human health.
- Fusing remote-sensed LCLUC and climate data with weather models can improve extreme heat forecasting and climate projections.
- NASA’s Earth Observation platforms can enable the operationalization of monitoring and forecasting of extreme heat and guide adaptations to reduce harm to improve health.
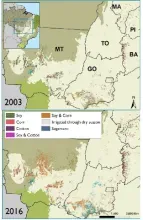
Characterizing land-use transitions helps combat climate change impacts and informs land-use policy
- The most biologically diverse savanna on earth is a major frontier of LCLUC
- It is yet unknown where high-impact land-use transitions are concentrated and the main drivers of those changes
- Urgent need to develop detection methods and novel data sets to inform decision-making a to address biodiversity loss and mitigate climate change impacts
- Use of Earth Observation data, time series analyses, and machine learning algorithms to expand the spatial and temporal data on agricultural development and a novel data set on irrigated agriculture in combination with spatial analyses of socioeconomic influences

DIFFERENT APPROACH TO U.S. DRUG POLICY NEEDED TO MEET CONSERVATION GOALS
- Counterdrug interdiction pushes cocaine trafficking into biodiverse landscapes.
- Analyses integrating remote sensing and socioeconomic data can identify and quantify land use/cover-change caused by illicit economies.
- Urgent need for such analyses to inform action to mitigate climate change and biodiversity loss in Central America.
- NASA’s role in Earth observation is essential for evaluating long-running U.S. policies.
- Long-term effects of U.S. drug policy undermine international conservation efforts.

POTENTIAL INCREASES IN WATER SCARCITY AS THE AGRICULTURAL SECTOR ADAPTS
- Water scarcity in agricultural regions is worsening as the Earth warms.
- Urgent need for local and regional analyses to formulate precision adaptation measures.
- Analyses integrating remote sensing, hydrological modeling, and economic modeling can
project future water scarcity and farmers’ responses via crop choice and irrigation investment. - NASA’s Earth observations are critical to track short-term (crop growth and seasonal water
use) and long-term (crop system transitions, irrigation investment) agricultural responses to
drought and target climate adaptation measures.
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 4